Handle form submissions with Node.js
Learn how to handle form submissions in Node.js using the Forminit SDK.
Form Backend API for Node.js
Section titled “Form Backend API for Node.js”Forminit is a form backend service that handles form submissions, data storage, and notifications — so you don’t have to.
With Forminit, you get all of this out of the box:
- No database required — Submissions are stored securely in Forminit’s infrastructure
- Built-in email notifications — Get notified instantly when forms are submitted
- Automatic validation — Email, phone, URL, and country fields are validated server-side
- File upload handling — Accept files up to 25 MB without configuring storage
- Spam protection — Integrates with reCAPTCHA, hCaptcha, and honeypot
- UTM tracking — Automatically capture marketing attribution data
- Dashboard access — View, search, and export submissions from a web interface
- Webhook support — Forward submissions to your own systems when needed
Forminit reduces form backend development from days to minutes. Focus on your application logic while Forminit handles the infrastructure.
Prerequisites
Section titled “Prerequisites”Before integrating Forminit with your Node.js application:
- Create a Forminit account at forminit.com
- Create a form in your dashboard
- Create an API key
1. Install
Section titled “1. Install”# npm
npm install forminit
# yarn
yarn add forminit
# pnpm
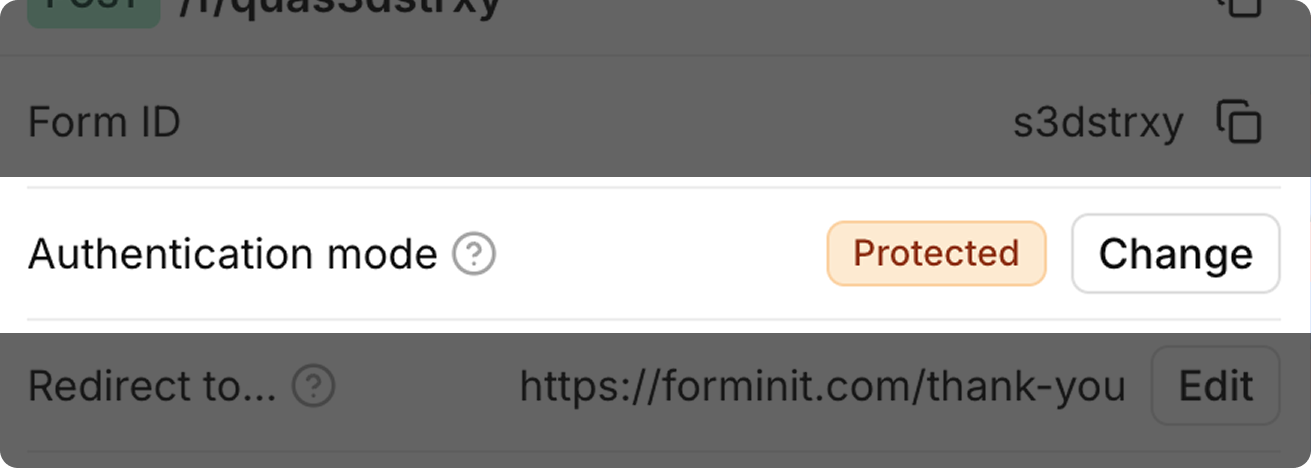
pnpm add forminit2. Set Authentication Mode to Protected
Section titled “2. Set Authentication Mode to Protected”Set authentication to Protected for server-side integrations. This enables higher rate limits and requires the x-api-key header.
3. Create an API Token and Add to Environment
Section titled “3. Create an API Token and Add to Environment”Generate your secret API token from Account → API Tokens in the Forminit dashboard.
# .env
FORMINIT_API_KEY="fi_your_secret_api_key"4. Send a Form Submission
Section titled “4. Send a Form Submission”Forminit uses a block-based system to structure form data. Each submission contains an array of blocks representing different field types.
For complete documentation on all available blocks, field naming conventions, and validation rules, see the Form Blocks Reference.
Forminit supports two submission formats: FormData and JSON.
FormData Submission
Section titled “FormData Submission”Best for forms with file uploads or when processing HTML form data:
import { Forminit } from 'forminit';
const forminit = new Forminit({
apiKey: process.env.FORMINIT_API_KEY,
});
const FORM_ID = 'frm_abc123xyz';
const formData = new FormData();
formData.append('fi-sender-firstName', 'John');
formData.append('fi-sender-lastName', 'Doe');
formData.append('fi-sender-email', 'john@example.com');
formData.append('fi-text-message', 'Hello world');
const { data, redirectUrl, error } = await forminit.submit(FORM_ID, formData);
if (error) {
console.error('Submission failed:', error.message);
return;
}
console.log('Submission successful:', data.hashId);FormData Field Naming:
| Block Type | Pattern | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Sender properties | fi-sender-{property} | fi-sender-email |
| Field blocks | fi-{type}-{name} | fi-text-message |
JSON Submission
Section titled “JSON Submission”Best for programmatic submissions with structured data:
import { Forminit } from 'forminit';
const forminit = new Forminit({
apiKey: process.env.FORMINIT_API_KEY,
});
const FORM_ID = 'frm_abc123xyz';
const { data, redirectUrl, error } = await forminit.submit(FORM_ID, {
blocks: [
{
type: 'sender',
properties: {
email: 'john@example.com',
firstName: 'John',
lastName: 'Doe',
phone: '+12025550123',
company: 'Acme Corp',
},
},
{
type: 'text',
name: 'message',
value: 'I would like to learn more about your services.',
},
{
type: 'select',
name: 'plan',
value: 'Enterprise',
},
{
type: 'rating',
name: 'urgency',
value: 4,
},
],
});
if (error) {
console.error('Submission failed:', error.message);
return;
}
console.log('Submission ID:', data.hashId);
console.log('Submitted at:', data.date);File Uploads
Section titled “File Uploads”File uploads require FormData and multipart handling. Here’s an example using Express with Multer:
import express from 'express';
import multer from 'multer';
import { Forminit } from 'forminit';
const app = express();
const upload = multer({ storage: multer.memoryStorage() });
const forminit = new Forminit({
apiKey: process.env.FORMINIT_API_KEY,
});
const FORM_ID = 'frm_abc123xyz';
app.post('/apply', upload.fields([
{ name: 'resume', maxCount: 1 },
{ name: 'documents', maxCount: 5 }
]), async (req, res) => {
const formData = new FormData();
formData.append('fi-sender-firstName', req.body.firstName);
formData.append('fi-sender-lastName', req.body.lastName);
formData.append('fi-sender-email', req.body.email);
formData.append('fi-text-cover_letter', req.body.coverLetter);
if (req.files.resume) {
const file = req.files.resume[0];
formData.append('fi-file-resume', new Blob([file.buffer]), file.originalname);
}
if (req.files.documents) {
for (const file of req.files.documents) {
formData.append('fi-file-documents', new Blob([file.buffer]), file.originalname);
}
}
const { data, error } = await forminit.submit(FORM_ID, formData);
if (error) {
return res.status(400).json({ success: false, message: error.message });
}
res.json({ success: true, submissionId: data.hashId });
});
app.listen(3000);File Upload Limits:
| Limit | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum upload size per submission | 25 MB |
| Maximum file blocks per submission | 20 |
Response Structure
Section titled “Response Structure”Success Response
Section titled “Success Response”The SDK returns { data, redirectUrl, error }. On successful submission:
const { data, redirectUrl, error } = await forminit.submit(FORM_ID, payload);
// data contains:
{
"hashId": "7LMIBoYY74JOCp1k",
"date": "2026-01-01 21:10:24",
"blocks": {
"sender": {
"firstName": "John",
"lastName": "Doe",
"email": "john.doe@example.com"
},
"message": "Hello world",
"plan": "Enterprise"
}
}
// redirectUrl contains the thank you page URL
"https://forminit.com/thank-you"| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
data.hashId | string | Unique submission identifier |
data.date | string | Submission timestamp (YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss) |
data.blocks | object | All submitted field values |
redirectUrl | string | Thank you page URL |
Error Response
Section titled “Error Response”When submission fails, error contains:
{
"error": "FI_SCHEMA_FORMAT_EMAIL",
"code": 400,
"message": "Invalid email format for field: 'contact'. Please enter a valid email address."
}| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
error | string | Error code identifier |
code | number | HTTP status code |
message | string | Human-readable error message |
Error Handling
Section titled “Error Handling”Always wrap submissions in try-catch and handle errors appropriately:
import { Forminit } from 'forminit';
const forminit = new Forminit({
apiKey: process.env.FORMINIT_API_KEY,
});
async function submitContactForm(formData) {
try {
const { data, redirectUrl, error } = await forminit.submit('frm_abc123xyz', formData);
if (error) {
switch (error.error) {
case 'FI_SCHEMA_FORMAT_EMAIL':
return { success: false, field: 'email', message: 'Invalid email address' };
case 'FI_RULES_PHONE_INVALID':
return { success: false, field: 'phone', message: 'Invalid phone number format' };
case 'TOO_MANY_REQUESTS':
return { success: false, message: 'Please wait before submitting again' };
default:
return { success: false, message: error.message };
}
}
return {
success: true,
submissionId: data.hashId,
redirectUrl,
};
} catch (err) {
console.error('Submission error:', err);
return { success: false, message: 'An unexpected error occurred' };
}
}Common Error Codes
Section titled “Common Error Codes”| Error Code | HTTP Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
FORM_NOT_FOUND | 404 | Form ID doesn’t exist or was deleted |
FORM_DISABLED | 403 | Form is disabled by owner |
MISSING_API_KEY | 401 | API key required but not provided |
EMPTY_SUBMISSION | 400 | No fields with values submitted |
FI_SCHEMA_FORMAT_EMAIL | 400 | Invalid email format |
FI_RULES_PHONE_INVALID | 400 | Invalid phone number format |
FI_SCHEMA_RANGE_RATING | 400 | Rating not between 1-5 |
FI_DATA_COUNTRY_INVALID | 400 | Invalid country code |
TOO_MANY_REQUESTS | 429 | Rate limit exceeded |
TypeScript Support
Section titled “TypeScript Support”The SDK includes TypeScript definitions:
import { Forminit } from 'forminit';
interface ContactFormData {
firstName: string;
lastName: string;
email: string;
message: string;
}
const forminit = new Forminit({
apiKey: process.env.FORMINIT_API_KEY!,
});
async function submitContact(formData: ContactFormData) {
const { data, redirectUrl, error } = await forminit.submit('frm_abc123xyz', {
blocks: [
{
type: 'sender',
properties: {
email: formData.email,
firstName: formData.firstName,
lastName: formData.lastName,
},
},
{
type: 'text',
name: 'message',
value: formData.message,
},
],
});
if (error) {
throw new Error(error.message);
}
return data;
}Rate Limits
Section titled “Rate Limits”Authenticated requests are limited to 5 requests per second.
When rate limited, you’ll receive a 429 status code:
{
"error": "TOO_MANY_REQUESTS",
"code": 429,
"message": "Rate limit exceeded. Maximum 5 requests per second allowed.",
"suggest": "Wait a moment before making another request."
}Security Best Practices
Section titled “Security Best Practices”- Store API keys in environment variables — Never hardcode keys in source code
- Use
.gitignore— Exclude.envfiles from version control - Validate input server-side — Don’t rely solely on client-side validation
- Use HTTPS — Always use secure connections in production
- Implement rate limiting — Protect your endpoints from abuse
- Sanitize user input — Prevent injection attacks
function validateContactForm(data) {
const errors = [];
if (!data.email || !/^[^\s@]+@[^\s@]+\.[^\s@]+$/.test(data.email)) {
errors.push('Valid email is required');
}
if (!data.firstName || data.firstName.length < 1) {
errors.push('First name is required');
}
if (!data.message || data.message.length < 10) {
errors.push('Message must be at least 10 characters');
}
return errors;
}Optional Integrations
Section titled “Optional Integrations”Enhance your forms with additional security:
- reCAPTCHA: forminit.com/docs/recaptcha/
- hCaptcha: forminit.com/docs/hcaptcha/
- Honeypot: forminit.com/docs/honeypot/
Related Documentation
Section titled “Related Documentation”- Form Blocks Reference — Complete reference for all block types
- File Uploads — Detailed file upload guide
- API Reference — Full REST API documentation
- Next.js Integration — Next.js specific setup
- Nuxt.js Integration — Nuxt.js specific setup
Was this page helpful?
Thanks for your feedback.